Dynegy Inc. South Bay Power
Location: San Diego, California



Summary
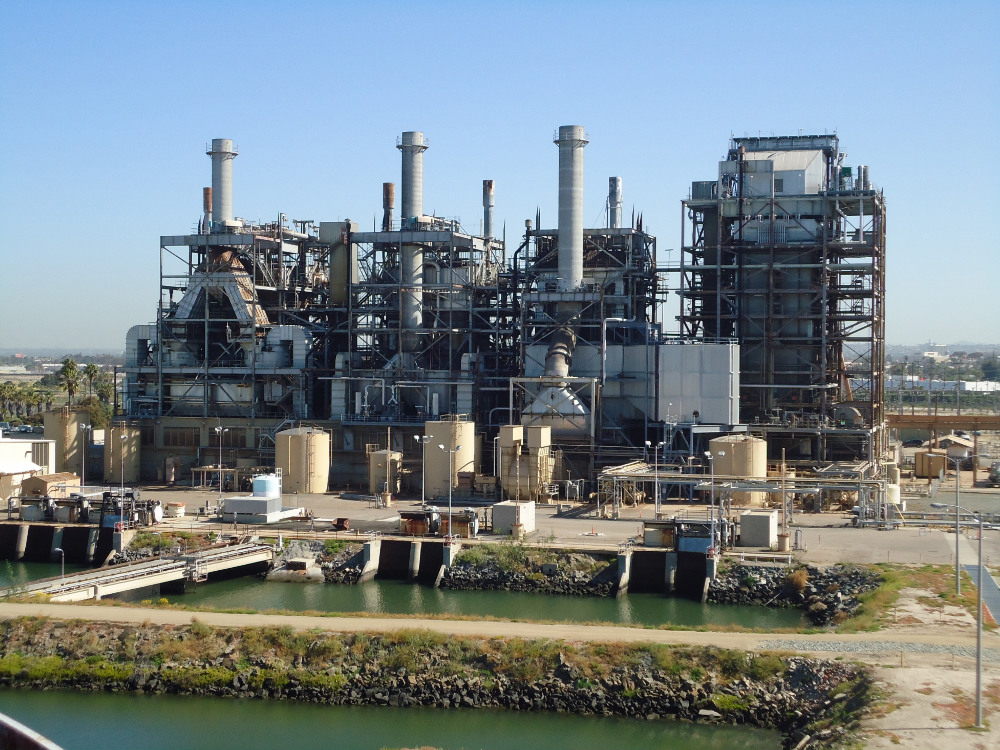
Dynegy was closing a 309-megawatt, natural gas fired facility equipped with a once-through cooling system. In preparation for demolition and remediation, NRC was selected to remove No. 6 crude oil that remained in two 5.5-million-gallon aboveground storage tanks (ASTs). Due to the complexity of the project, the work scope was divided into more manageable task components, as follows: dewatering, pipe cleaning, pump station and equipment decontamination, tank access, cribbing installation, tank bottom removal, solidification, roof pontoon washing, tank cleaning, filter removal and boiler front flushing.
Once on site, out-of-scope challenges became immediately apparent including undocumented water accumulating inside tanks and a 140-foot diameter “Hidek” floating roof structure that had partially collapsed as a result of rainwater accumulating on its exposed surface.
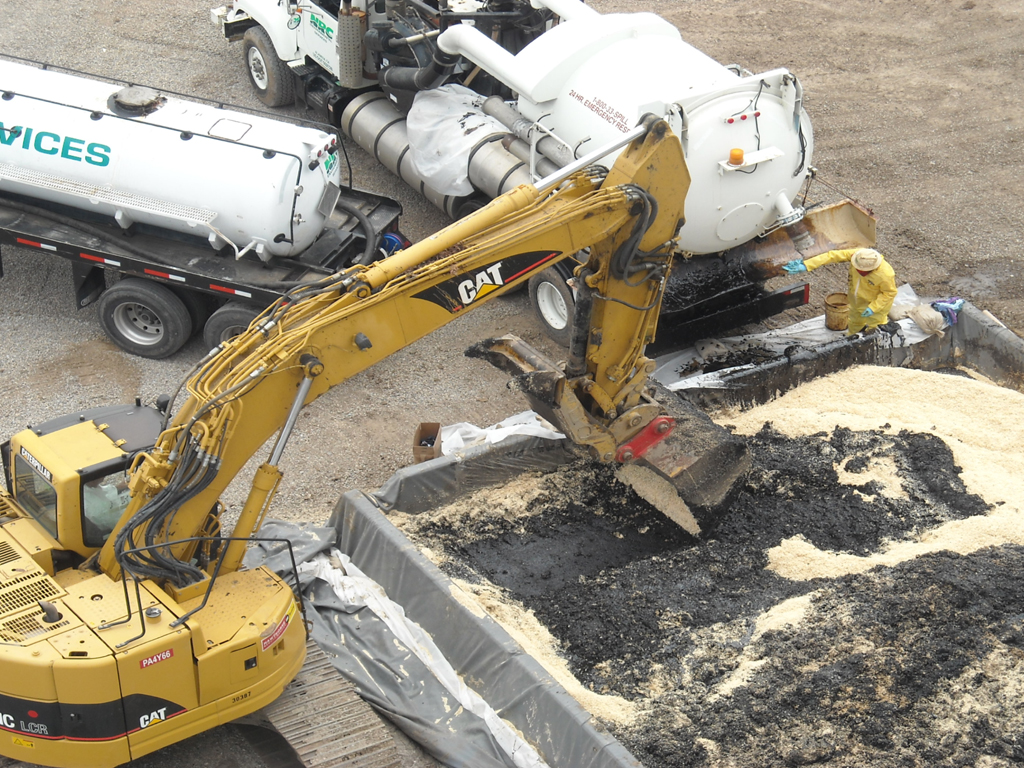
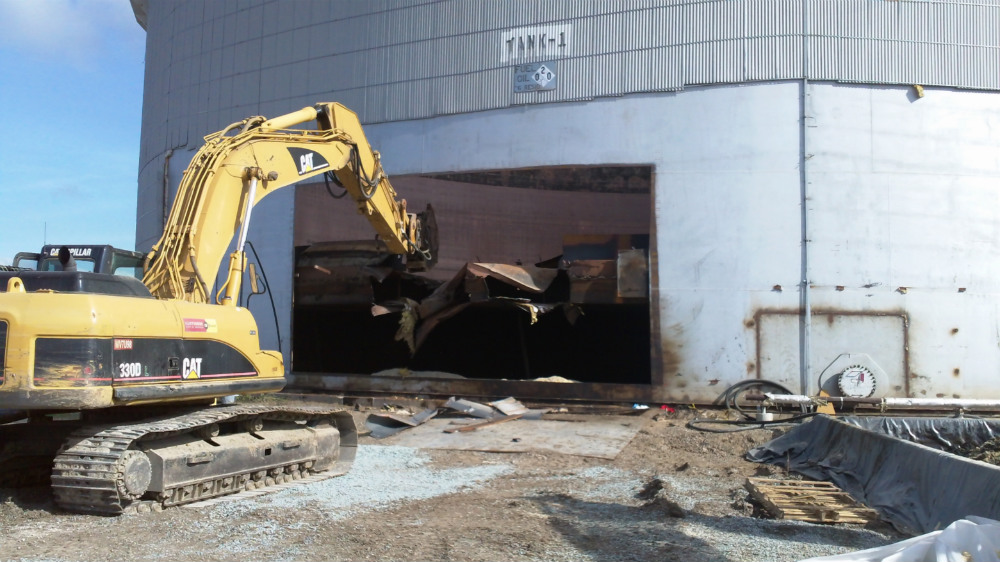
Field work began with lead/asbestos abatement, recovery of water co-mingled with crude oil from the interior of ASTs and roof dewatering operations. This was followed by cutter stock/hot water flushing and air drying of 40 burner fronts, six electrically driven 10” pumps and approximately 8,811 linear feet of 2”-10” carbon steel fuel oil supply, return and recirculation piping. Immediately following, ASTs were accessed via abrasive water jet cutting technology and tank bottom sediment/sludge recovery via low profile skid loader(s) and other heavy equipment. Subject tank bottoms were promptly transferred into a 40-mil HDPE lined 40’ X 40’ treatment cell and solidified with dry saw dust. Wood timber cribbing was installed in one AST to permit safe entry while the other tank required demolition of the partially collapsed roof utilizing a track operated excavator equipped with shear system.
Next interior tank surfaces were inoculated with a suitable surfactant/detergent solution, agitated via scrubbing and rinsed in triplicate utilizing a high pressure/high temperature wash system.
32,000 gallons of non-RCRA hazardous waste fuel oil and water, and 150,000 gallons of non-hazardous wastewater were recovered utilizing vacuum equipped tanker trucks and transported off site for disposal. Roughly 1,000 tons of solidified fuel oil were loaded onto lined truck and transfer units and transported off site for landfill disposal. Nearly 120 tons of scrap iron and metal, generated as a result of the floating roof demolition, were saturated with a suitable surfactant/detergent, triple rinsed, loaded into 40 cubic yard (CY) roll-off bin containers and transported off site for recycle. All tanks and piping were subsequently deemed “gas-free” by an independent testing organization.
Highlights
- No. 6 crude oil solidification.
- Removal of 32,000 gallons of non-RCRA hazardous waste fuel oil and water.
- 150,000 gallons of non-hazardous wastewater recovered.
- ~120 tons of scrap metal recycled.

 Search
Search Menu
Menu